whoami
The whoami command will display the current user account name of the logged in user.
echo
the echo command can be used to display information on output . Output can be set to the command line, stdout, stdin, or pip to another command
—insert pic–
pwd
The pwd will display the present working directory, which is the relative path of the directory where commands will be run.
cd
change directory command is used to change the directory location.
su
Switch user command to switch between user accounts
using the – (minus) is used to change to the root user. The password prompt will appear when switching into another user account.
exit
The exit command will will logout of the current user. If su was used will return to the user that was previously logged in until no user at which time it will log out of linux.
hostname
the hostname command will retrieve the hostname in raspian, which by default is [raspberrypi].
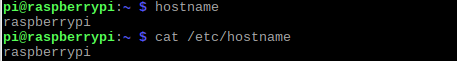
this can be changed by typing the desired name after hostname command.
hostnamectl
echo NodePiZero > hostname
cat /etc/hostname
Close terminal window and open and the new hostname should appear
—insert pic—
To add the hostname to other computers the name will need to be added to the hostfile or if available DNS.
Hosts
The hosts file can be found
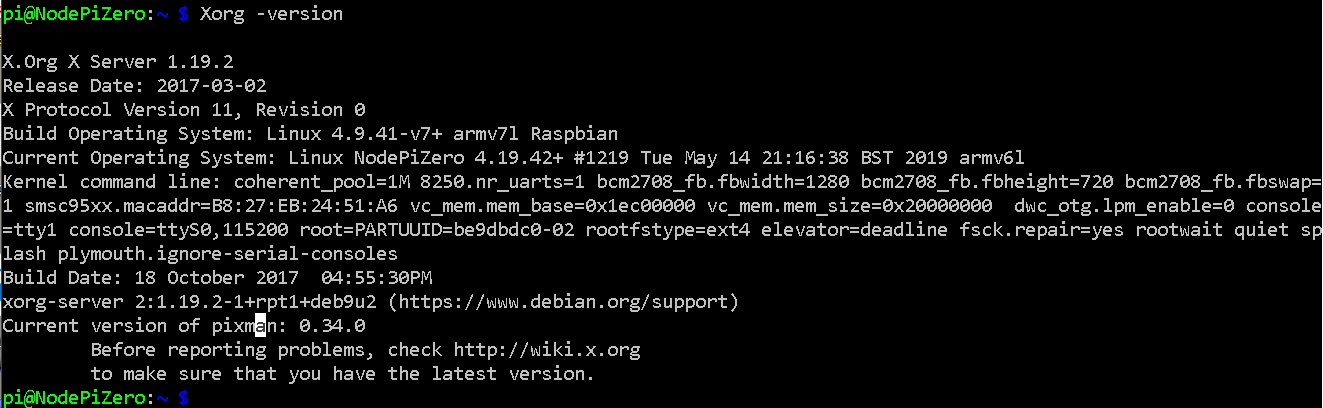
X-Server
To get the Version:
Xorg – version
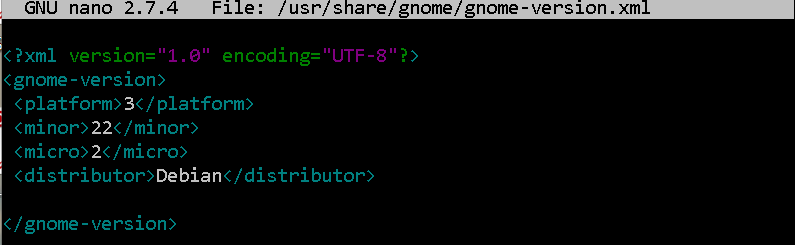
GNOME
GNOME 3 version is stored in this file:
/usr/share/gnome/gnome-version.xml
Package Installation
Compiling Software From Source
Tarball
To uncompress file use the tar command
tar -xzvf filename.tar.gz -C /[Directory/Path]
The file may include a setup script file, Look for /[Directory/Path]/bin/somescript.sh
The file should include any steps required for setup such as making directories and compiling any uncompressed code to binaries .
Example: Installing Jira on Raspian.
Repositories
apt-get
apt-cache
Server/Configuration Management
-Puppet
-Chef
Files
touch
the touch command can be used to create files
mkdir
make directory command will create a new directory, either relative to pwd or in declared absolute path.
ls
List command will display a list of files and directories. The command can list relative or absolute directory information.
— insert pic—
it can display as a list matrix or column directory information.
— insert pic —
chmod
change modes command allows modification of how files and directories are accessed.
—insert pic of permissions —
chown
change owner command allows the user that owns a file to be changed.
chown new_user_owner file_name
chgrp
change group command allows the group that owns a file to be changed.
chgrp new_group_name_assigned file_name
useradd
add new user command can be used to add new users
groupadd
Add new group command used to add new groups
setfacl
setfacl -m u:susie:rw file3
getfacl
umask
used to determine default permissions when not exclusively declared when creating files or directories.
default is 022 , this is subtracted from 666 to get permission settings.
can be changed
